
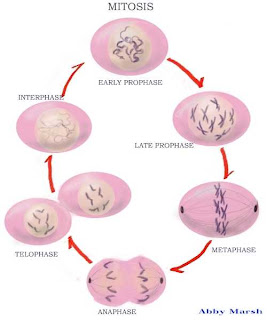

The two key differences in the division of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are that: Chromosomes are much more complex structures than the single cyclic DNA molecule of prokaryotes, which makes the processes of replication and segregation far more complex. Signals of initiation of cell division in them come mainly from the needs of the entire multicellular organism.Įukaryotic cells have a larger genome than prokaryotes. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotes do not begin to divide whenever external conditions are favorable. Тhе eukaryotic cells divide by mitosis or meiosis.Ĭell division of eukaryotic cells undergoes the same four basic steps as for prokaryotes, but due to their more complex structure, these processes are also more complex. Finally, each newly formed cell builds a new cell wall around its plasma membrane. This ring is shrinking and provides for the final separation of the two new cells.

The two new replication points are spaced apart and a new plasma membrane begins to build between them. The first area of the DNA molecule that replicates is the replication point. DNA Segregation: As a result of the DNA replication and the continued elongation of the maternal cell the daughter genomes are actively distancing from each other.The new “daughter” genomes separate from each other during replication, remaining attached to the plasma membrane with their replication points. This replication point is attached to the plasma membrane and starts copying the DNA molecule. There is a specific area in it called a replication point, consisting of more than 22 different proteins. Replication of DNA: The genome of prokaryotes is represented by a cyclic DNA molecule.Receiving a reproduction signal: Usually, external factors (presence of nutrients, appropriate temperature) control binary fusion.In prokaryotes, division results in the reproduction of the entire unicellular organism.įour major events occur in the cell, in order to divide: The cell increases its size, doubles its genetic information, and then divides into two new daughter cells.
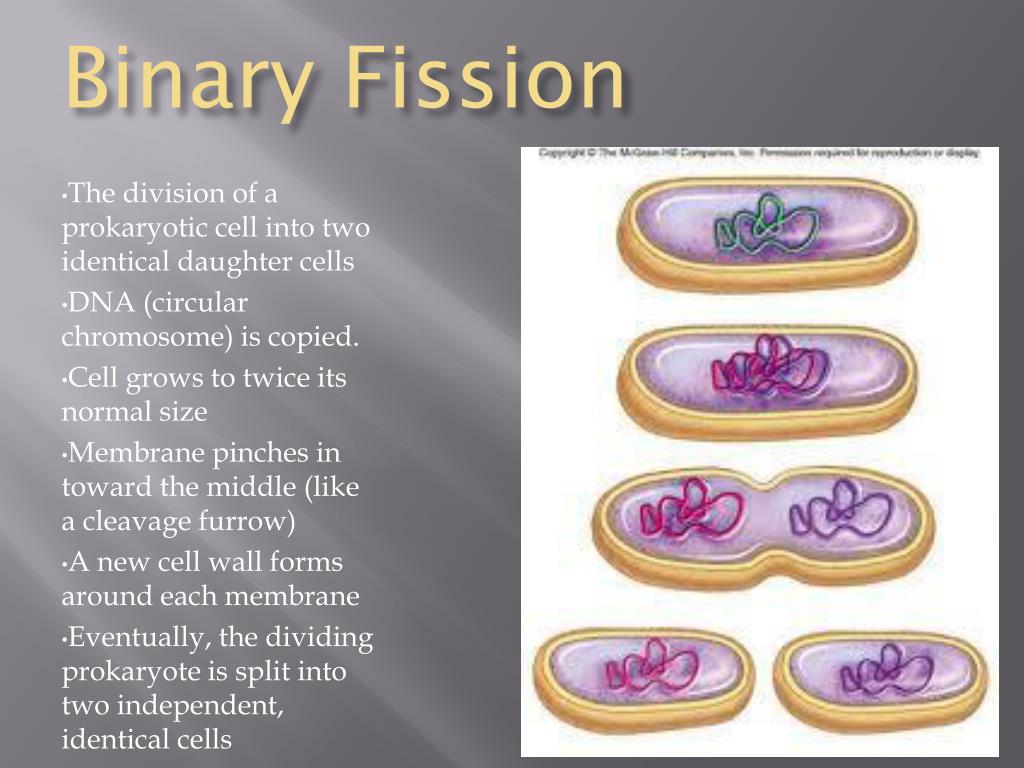
The binary fusion is a process of dividing the cell into two identical or almost identical halves. Prokaryotic cells are divided by simple division, called binary fusion. The cells are propagated by division – a process in which the content of the mother cell is divided into two newly-derived daughter cells. Similarities Between Binary Fission and Cell Division


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
